X-ray diffraction
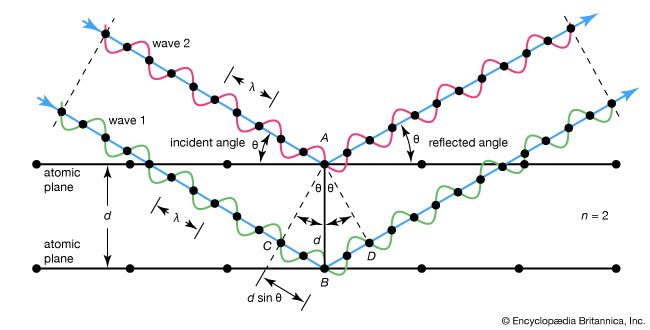
X-ray diffraction, phenomenon in which the atoms of a crystal, by virtue of their uniform spacing, cause an interference pattern of the waves present in an incident beam of X-rays. The atomic planes of the crystal act on the X-rays in exactly the same manner as does a uniformly ruled diffraction grating on a beam of light. A beam of X-rays contacts a crystal with an angle of incidence θ. It is reflected off the atoms of the crystal with the same angle θ. The X-rays reflect off atomic planes in the crystal that are a distance d apart. The X-rays reflecting off two different planes must interfere constructively to form an interference pattern; otherwise, the X-rays would interfere destructively and form no pattern. To interfere constructively, the difference in path length between the beams reflecting off two atomic planes must be a whole number (n) of wavelengths (λ), or nλ. This leads to the Bragg law nλ = 2d sin θ. By observing the interference pattern, the internal structure of the crystal can be deduced. See also Bragg law; Laue diffraction pattern.
-
How do scientists use X-ray diffraction to discover the structure of DNA?
-
What is the Bragg law and why is it important in crystallography?
-
How are X-rays produced in a laboratory?
-
What other techniques do scientists use to study the atomic structure of materials?
-
How did the discovery of X-ray diffraction change our understanding of chemistry?